SKU:RB-02S113 九轴姿态检测传感器
来自ALSROBOT WiKi
目录 |
产品概述
九轴姿态检测传感器基于MPU-9150开发而成,MPU-9150是世界上第一款集成了三轴陀螺仪、三轴加速度计及三轴磁力计的芯片。MPU-9150主要应用于低功耗、低价格和高性能消费电子产品,包含智能手机、平板电脑和可穿戴设备中。MPU-9150包含三个16位ADC用于陀螺仪信号进行数字化输出、三个16位ADC用于加速度计信号数字化输出及三个13位ADC用于磁力计信号数字化输出。九轴姿态检测传感器可广泛应用于航模无人机,机器人,天线云台,聚光太阳能,地面及水下设备,虚拟现实,人体运动分析等需要低成本、高动态三维姿态测量的产品设备中。
规格参数
- 工作电压:5V
- 接口类型:IIC通讯接口
- 输出信号:数字信号
- 工作温度:-5℃到75℃
- 接口类型:KF2510-4P防插反接口
- 通信接口:IIC 通信
- 三轴陀螺仪量程可由用户设定,包含±250, ±500, ±1000, and ±2000°/sec
- 三轴加速度量程可由用户设定,包含±2g, ±4g, ±8g and ±16g
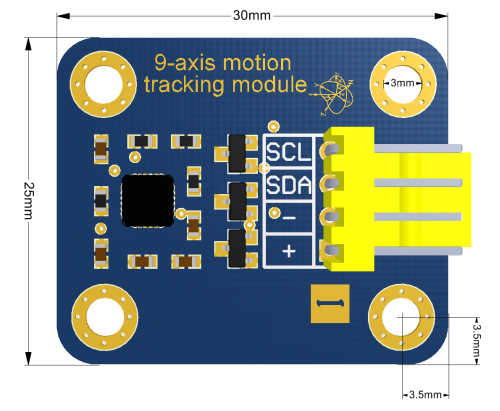
- 产品尺寸:30mm x 25mm
- 固定孔尺寸:23mm x 18mm
- 重量大小:3g
- 工作电流:20mA
- 安装:4 * M3 定位孔
- 产品尺寸:
- 引脚定义:
(1)-:电源地
(2)+:电源正极
(3)SDA:IIC数据信号
(4)SCL:IIC时钟信号
使用方法
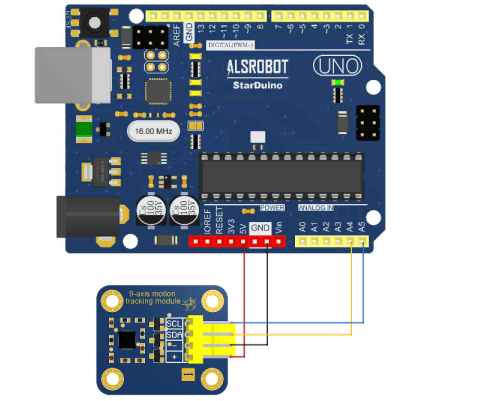
- 硬件环境:
(1)Starduino UNO R3 控制器
(2)4P 传感器连接线
(3)9轴姿态传感器
- 软件环境:Arduino IDE 1.8.1
- 硬件连接
- 例子程序:
#include "Wire.h"
// I2Cdev and MPU9250 must be installed as libraries, or else the .cpp/.h files
// for both classes must be in the include path of your project
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU9250.h"
// class default I2C address is 0x68
// specific I2C addresses may be passed as a parameter here
// AD0 low = 0x68 (default for InvenSense evaluation board)
// AD0 high = 0x69
MPU9250 accelgyro;
I2Cdev I2C_M;
uint8_t buffer_m[6];
int16_t ax, ay, az;
int16_t gx, gy, gz;
int16_t mx, my, mz;
float heading;
float tiltheading;
float Axyz[3];
float Gxyz[3];
float Mxyz[3];
#define sample_num_mdate 5000
volatile float mx_sample[3];
volatile float my_sample[3];
volatile float mz_sample[3];
static float mx_centre = 0;
static float my_centre = 0;
static float mz_centre = 0;
volatile int mx_max =0;
volatile int my_max =0;
volatile int mz_max =0;
volatile int mx_min =0;
volatile int my_min =0;
volatile int mz_min =0;
void setup() {
// join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn't do this automatically)
Wire.begin();
// initialize serial communication
// (38400 chosen because it works as well at 8MHz as it does at 16MHz, but
// it's really up to you depending on your project)
Serial.begin(38400);
// initialize device
Serial.println("Initializing I2C devices...");
accelgyro.initialize();
// verify connection
Serial.println("Testing device connections...");
Serial.println(accelgyro.testConnection() ? "MPU9250 connection successful" : "MPU9250 connection failed");
delay(1000);
Serial.println(" ");
//Mxyz_init_calibrated ();
}
void loop()
{
getAccel_Data();
getGyro_Data();
getCompassDate_calibrated(); // compass data has been calibrated here
getHeading(); //before we use this function we should run 'getCompassDate_calibrated()' frist, so that we can get calibrated data ,then we can get correct angle .
getTiltHeading();
Serial.println("calibration parameter: ");
Serial.print(mx_centre);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(my_centre);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(mz_centre);
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println("Acceleration(g) of X,Y,Z:");
Serial.print(Axyz[0]);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(Axyz[1]);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(Axyz[2]);
Serial.println("Gyro(degress/s) of X,Y,Z:");
Serial.print(Gxyz[0]);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(Gxyz[1]);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(Gxyz[2]);
Serial.println("Compass Value of X,Y,Z:");
Serial.print(Mxyz[0]);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(Mxyz[1]);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(Mxyz[2]);
Serial.println("The clockwise angle between the magnetic north and X-Axis:");
Serial.print(heading);
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println("The clockwise angle between the magnetic north and the projection of the positive X-Axis in the horizontal plane:");
Serial.println(tiltheading);
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println(" ");
delay(300);
}
void getHeading(void)
{
heading=180*atan2(Mxyz[1],Mxyz[0])/PI;
if(heading <0) heading +=360;
}
void getTiltHeading(void)
{
float pitch = asin(-Axyz[0]);
float roll = asin(Axyz[1]/cos(pitch));
float xh = Mxyz[0] * cos(pitch) + Mxyz[2] * sin(pitch);
float yh = Mxyz[0] * sin(roll) * sin(pitch) + Mxyz[1] * cos(roll) - Mxyz[2] * sin(roll) * cos(pitch);
float zh = -Mxyz[0] * cos(roll) * sin(pitch) + Mxyz[1] * sin(roll) + Mxyz[2] * cos(roll) * cos(pitch);
tiltheading = 180 * atan2(yh, xh)/PI;
if(yh<0) tiltheading +=360;
}
void Mxyz_init_calibrated ()
{
Serial.println(F("Before using 9DOF,we need to calibrate the compass frist,It will takes about 2 minutes."));
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(F("During calibratting ,you should rotate and turn the 9DOF all the time within 2 minutes."));
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(F("If you are ready ,please sent a command data 'ready' to start sample and calibrate."));
while(!Serial.find("ready"));
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println("ready");
Serial.println("Sample starting......");
Serial.println("waiting ......");
get_calibration_Data ();
Serial.println(" ");
Serial.println("compass calibration parameter ");
Serial.print(mx_centre);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(my_centre);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(mz_centre);
Serial.println(" ");
}
void get_calibration_Data ()
{
for (int i=0; i<sample_num_mdate;i++)
{
get_one_sample_date_mxyz();
/*
Serial.print(mx_sample[2]);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(my_sample[2]); //you can see the sample data here .
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(mz_sample[2]);
*/
if (mx_sample[2]>=mx_sample[1])mx_sample[1] = mx_sample[2];
if (my_sample[2]>=my_sample[1])my_sample[1] = my_sample[2]; //find max value
if (mz_sample[2]>=mz_sample[1])mz_sample[1] = mz_sample[2];
if (mx_sample[2]<=mx_sample[0])mx_sample[0] = mx_sample[2];
if (my_sample[2]<=my_sample[0])my_sample[0] = my_sample[2];//find min value
if (mz_sample[2]<=mz_sample[0])mz_sample[0] = mz_sample[2];
}
mx_max = mx_sample[1];
my_max = my_sample[1];
mz_max = mz_sample[1];
mx_min = mx_sample[0];
my_min = my_sample[0];
mz_min = mz_sample[0];
mx_centre = (mx_max + mx_min)/2;
my_centre = (my_max + my_min)/2;
mz_centre = (mz_max + mz_min)/2;
}
void get_one_sample_date_mxyz()
{
getCompass_Data();
mx_sample[2] = Mxyz[0];
my_sample[2] = Mxyz[1];
mz_sample[2] = Mxyz[2];
}
void getAccel_Data(void)
{
accelgyro.getMotion9(&ax, &ay, &az, &gx, &gy, &gz, &mx, &my, &mz);
Axyz[0] = (double) ax / 16384;//16384 LSB/g
Axyz[1] = (double) ay / 16384;
Axyz[2] = (double) az / 16384;
}
void getGyro_Data(void)
{
accelgyro.getMotion9(&ax, &ay, &az, &gx, &gy, &gz, &mx, &my, &mz);
Gxyz[0] = (double) gx * 250 / 32768;
Gxyz[1] = (double) gy * 250 / 32768;
Gxyz[2] = (double) gz * 250 / 32768;
}
void getCompass_Data(void)
{
I2C_M.writeByte(MPU9150_RA_MAG_ADDRESS, 0x0A, 0x01); //enable the magnetometer
delay(10);
I2C_M.readBytes(MPU9150_RA_MAG_ADDRESS, MPU9150_RA_MAG_XOUT_L, 6, buffer_m);
mx = ((int16_t)(buffer_m[1]) << 8) | buffer_m[0] ;
my = ((int16_t)(buffer_m[3]) << 8) | buffer_m[2] ;
mz = ((int16_t)(buffer_m[5]) << 8) | buffer_m[4] ;
//Mxyz[0] = (double) mx * 1200 / 4096;
//Mxyz[1] = (double) my * 1200 / 4096;
//Mxyz[2] = (double) mz * 1200 / 4096;
Mxyz[0] = (double) mx * 4800 / 8192;
Mxyz[1] = (double) my * 4800 / 8192;
Mxyz[2] = (double) mz * 4800 / 8192;
}
void getCompassDate_calibrated ()
{
getCompass_Data();
Mxyz[0] = Mxyz[0] - mx_centre;
Mxyz[1] = Mxyz[1] - my_centre;
Mxyz[2] = Mxyz[2] - mz_centre;
}
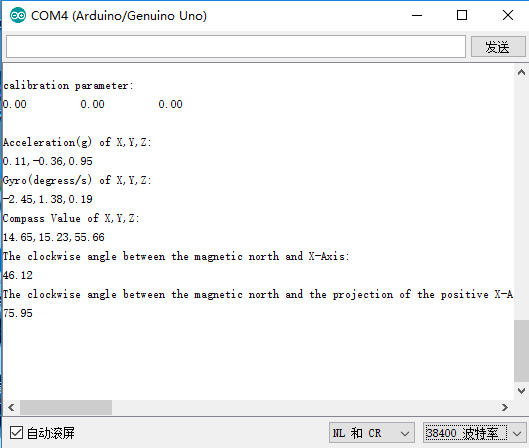
- 程序效果
将程序下载后,将九轴姿态检测传感器水平静止放置,打开串口监视器,波特率调整为38400,等待显示“Initializing I2C devices... Testing device connections... MPU9250 connection successful”后晃动传感器,观察数据变化。
相关推荐
例程下载
- 产品例子程序及库文件下载链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pK9ybyF 密码:i8hb