“(SKU:RB-02S073)LSM9DS0- 9轴姿态传感器”的版本间的差异
来自ALSROBOT WiKi
(→产品相关推荐) |
(→产品相关推荐) |
||
| (未显示1个用户的4个中间版本) | |||
| 第99行: | 第99行: | ||
==应用例程== | ==应用例程== | ||
===示例代码=== | ===示例代码=== | ||
| − | + | [https://github.com/sparkfun/SparkFun_LSM9DS0_Arduino_Library 库文件官方下载地址]<br/> | |
| − | + | <pre style='color:blue'> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | https://github.com/sparkfun/ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
#include <SPI.h> // Included for SFE_LSM9DS0 library | #include <SPI.h> // Included for SFE_LSM9DS0 library | ||
#include <Wire.h> | #include <Wire.h> | ||
#include <SFE_LSM9DS0.h> | #include <SFE_LSM9DS0.h> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
#define LSM9DS0_XM 0x1D // Would be 0x1E if SDO_XM is LOW | #define LSM9DS0_XM 0x1D // Would be 0x1E if SDO_XM is LOW | ||
#define LSM9DS0_G 0x6B // Would be 0x6A if SDO_G is LOW | #define LSM9DS0_G 0x6B // Would be 0x6A if SDO_G is LOW | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
LSM9DS0 dof(MODE_I2C, LSM9DS0_G, LSM9DS0_XM); | LSM9DS0 dof(MODE_I2C, LSM9DS0_G, LSM9DS0_XM); | ||
| − | + | const byte INT1XM = 2; // INT1XM tells us when accel data is ready | |
| − | + | const byte INT2XM = 3; // INT2XM tells us when mag data is ready | |
| − | // | + | const byte DRDYG = 4; // DRDYG tells us when gyro data is ready |
| − | + | boolean printRaw = true; | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
void setup() | void setup() | ||
{ | { | ||
| + | // Set up interrupt pins as inputs: | ||
| + | pinMode(INT1XM, INPUT); | ||
| + | pinMode(INT2XM, INPUT); | ||
| + | pinMode(DRDYG, INPUT); | ||
| + | |||
Serial.begin(115200); // Start serial at 115200 bps | Serial.begin(115200); // Start serial at 115200 bps | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
uint16_t status = dof.begin(); | uint16_t status = dof.begin(); | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Serial.println(status, HEX); | Serial.println(status, HEX); | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
void loop() | void loop() | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | + | printMenu(); | |
| − | + | while (!Serial.available()) | |
| − | + | parseMenu(Serial.read()); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
} | } | ||
| − | void | + | void printAccel() |
{ | { | ||
| − | + | if (digitalRead(INT1XM)) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | dof.readAccel(); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Serial.print("A: "); | |
| − | + | if (printRaw) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.ax); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.ay); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(dof.az); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | else | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.calcAccel(dof.ax)); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.calcAccel(dof.ay)); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(dof.calcAccel(dof.az)); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
} | } | ||
| − | void | + | void printGyro() |
{ | { | ||
| − | + | if (digitalRead(DRDYG)) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | dof.readGyro(); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Serial.print("G: "); | |
| − | + | if (printRaw) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.gx); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.gy); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(dof.gz); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | else | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.calcGyro(dof.gx)); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.calcGyro(dof.gy)); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(dof.calcGyro(dof.gz)); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
} | } | ||
void printMag() | void printMag() | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | + | if (digitalRead(INT2XM)) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | dof.readMag(); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Serial.print("M: "); | |
| − | + | if (printRaw) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.mx); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.my); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.mz); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(calcHeading(dof.mx, dof.my)); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | else | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.mx), 4); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.my), 4); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.mz), 4); | |
| − | + | Serial.print(", "); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(calcHeading(dof.mx, dof.my)); | |
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | float calcHeading(float hx, float hy) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | { | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
if (hy > 0) | if (hy > 0) | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | + | return 90 - (atan(hx / hy) * 180 / PI); | |
} | } | ||
else if (hy < 0) | else if (hy < 0) | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | + | return 270 - (atan(hx / hy) * 180 / PI); | |
} | } | ||
else // hy = 0 | else // hy = 0 | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | if (hx < 0) | + | if (hx < 0) return 180; |
| − | else | + | else return 0; |
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | void streamAll() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | if ((digitalRead(INT2XM)) && (digitalRead(INT1XM)) && | ||
| + | (digitalRead(DRDYG))) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | printAccel(); | ||
| + | printGyro(); | ||
| + | printMag(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | void setScale() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | char c; | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Set accelerometer scale:")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 2G")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 4G")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 6G")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t4) +/- 8G")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t5) +/- 16G")); | ||
| + | while (Serial.available() < 1) | ||
| + | ; | ||
| + | c = Serial.read(); | ||
| + | switch (c) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | case '1': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_2G); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '2': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_4G); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '3': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_6G); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '4': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_8G); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '5': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_16G); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | // Print the gyro scale ranges: | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Set gyroscope scale:")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 245 DPS")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 500 DPS")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 2000 DPS")); | ||
| + | // Wait for a character to come in: | ||
| + | while (Serial.available() < 1); | ||
| + | c = Serial.read(); | ||
| + | // Use the setGyroScale function to set the gyroscope | ||
| + | // full-scale range to any of the possible ranges. These ranges | ||
| + | // are all defined in SFE_LSM9DS0.h. | ||
| + | switch (c) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | case '1': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_245DPS); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '2': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_500DPS); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '3': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_2000DPS); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Set magnetometer scale:")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 2GS")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 4GS")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 8GS")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t4) +/- 12GS")); | ||
| + | while (Serial.available() < 1) | ||
| + | ; | ||
| + | c = Serial.read(); | ||
| + | switch (c) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | case '1': | ||
| + | dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_2GS); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '2': | ||
| + | dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_4GS); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '3': | ||
| + | dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_8GS); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '4': | ||
| + | dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_12GS); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | void setRaw() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | if (printRaw) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | printRaw = false; | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Printing calculated readings")); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | printRaw = true; | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Printing raw readings")); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | void setODR() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | char c; | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Set Accelerometer ODR (Hz):")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t1) 3.125 \t 6) 100")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t2) 6.25 \t 7) 200")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t3) 12.5 \t 8) 400")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t4) 25 \t 9) 800")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t5) 50 \t A) 1600")); | ||
| + | while (Serial.available() < 1) | ||
| + | ; | ||
| + | c = Serial.read(); | ||
| + | switch (c) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | case '1': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_3125); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '2': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_625); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '3': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_125); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '4': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_25); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '5': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_50); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '6': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_100); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '7': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_200); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '8': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_400); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '9': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_800); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case 'A': | ||
| + | case 'a': | ||
| + | dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_1600); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Set Gyro ODR/Cutoff (Hz):")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t1) 95/12.5 \t 8) 380/25")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t2) 95/25 \t 9) 380/50")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t3) 190/125 \t A) 380/100")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t4) 190/25 \t B) 760/30")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t5) 190/50 \t C) 760/35")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t6) 190/70 \t D) 760/50")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t7) 380/20 \t E) 760/100")); | ||
| + | while (Serial.available() < 1); | ||
| + | c = Serial.read(); | ||
| + | switch (c) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | case '1': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_95_BW_125); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '2': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_95_BW_25); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '3': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_125); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '4': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_25); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '5': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_50); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '6': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_70); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '7': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_20); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '8': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_25); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '9': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_50); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case 'A': | ||
| + | case 'a': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_100); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case 'B': | ||
| + | case 'b': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_30); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case 'C': | ||
| + | case 'c': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_35); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case 'D': | ||
| + | case 'd': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_50); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case 'E': | ||
| + | case 'e': | ||
| + | dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_100); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("Set Magnetometer ODR (Hz):")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t1) 3.125 \t 4) 25")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t2) 6.25 \t 5) 50")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("\t3) 12.5 \t 6) 100")); | ||
| + | while (Serial.available() < 1) | ||
| + | ; | ||
| + | c = Serial.read(); | ||
| + | switch (c) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | case '1': | ||
| + | dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_3125); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '2': | ||
| + | dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_625); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '3': | ||
| + | dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_125); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '4': | ||
| + | dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_25); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '5': | ||
| + | dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_50); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '6': | ||
| + | dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_100); | ||
| + | break; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| − | + | void printMenu() | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | void | + | |
{ | { | ||
| − | + | Serial.println(); | |
| + | Serial.println(F("////////////////////////////////////////////")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("// LSM9DS0 Super Awesome Amazing Fun Time //")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("////////////////////////////////////////////")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("1) Stream Accelerometer")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("2) Stream Gyroscope")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("3) Stream Magnetometer")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("4) Stream output from all sensors")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("5) Set Sensor Scales")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("6) Switch To/From Raw/Calculated Readings")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(F("7) Set Output Data Rates")); | ||
| + | Serial.println(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | // parseMenu() takes a char parameter, which should map to one of | |
| − | + | // the defined menu options. A switch statement will control what | |
| − | + | // happens based on the given character input. | |
| − | + | void parseMenu(char c) | |
| + | { | ||
| + | switch (c) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | case '1': | ||
| + | while(!Serial.available()) | ||
| + | printAccel(); // Print accelerometer values | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '2': | ||
| + | while(!Serial.available()) | ||
| + | printGyro(); // Print gyroscope values | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '3': | ||
| + | while(!Serial.available()) | ||
| + | printMag(); // Print magnetometer values | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '4': | ||
| + | while(!Serial.available()) | ||
| + | streamAll(); // Print all sensor readings | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '5': | ||
| + | setScale(); // Set the ranges of each sensor | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '6': | ||
| + | setRaw(); // Switch between calculated and raw output | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case '7': | ||
| + | setODR(); // Set the data rates of each sensor | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===程序效果=== | ===程序效果=== | ||
下载完程序,然后打开串口监视器,将波特率调到115200,然后按照显示的内容输入相应数字进行功能选择,可以观察到多种数据。 | 下载完程序,然后打开串口监视器,将波特率调到115200,然后按照显示的内容输入相应数字进行功能选择,可以观察到多种数据。 | ||
| 第373行: | 第528行: | ||
[http://www.makerspace.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=5505&fromuid=10780 Arduino 9 Axes Motion Shield 9轴运动扩展板 三轴加速度计]<br/> | [http://www.makerspace.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=5505&fromuid=10780 Arduino 9 Axes Motion Shield 9轴运动扩展板 三轴加速度计]<br/> | ||
===相关学习资料=== | ===相关学习资料=== | ||
| − | [https://www.sparkfun.com/videos#all/E4L8bYt6lCs/153 | + | [https://www.sparkfun.com/videos#all/E4L8bYt6lCs/153 LSM9DS0- 9轴姿态传感器应用视频]<br/> |
[https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/8/c/c/4/9/lsm9ds0_breakout-v10-schematic-.pdf 电路原理图]<br/> | [https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/8/c/c/4/9/lsm9ds0_breakout-v10-schematic-.pdf 电路原理图]<br/> | ||
[https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/f/6/1/f/0/LSM9DS0.pdf 数据表(lmv324)]<br/> | [https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/f/6/1/f/0/LSM9DS0.pdf 数据表(lmv324)]<br/> | ||
| − | [https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/lsm9ds0-hookup-guide | + | [https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/lsm9ds0-hookup-guide/advanced-arduino-example LSM9DS0- 9轴姿态传感器官方操作手册]<br/> |
[https://github.com/sparkfun/LSM9DS0_Breakout GitHub(设计文件)]<br/> | [https://github.com/sparkfun/LSM9DS0_Breakout GitHub(设计文件)]<br/> | ||
[http://www.makerspace.cn/portal.php 奥松机器人技术论坛]<br/> | [http://www.makerspace.cn/portal.php 奥松机器人技术论坛]<br/> | ||
2015年10月9日 (五) 11:43的最后版本
目录 |
产品概述
LSM9DS0-9轴姿态传感器选用的是LSM9DS0芯片,它是一种可实现动作感应的系统芯片,里面包括了一个3轴加速计,一个3轴陀螺仪和一个3轴磁力计。在LSM9DS0中,每种传感器都有良好的检测范围:LSM9DS0线性加速满量程为±2g/±4g/±6g/±8g/±16g;磁场满量程为±2 /±4 /±8 /±12高斯;陀螺仪满量程为±245 /±500 /±2000°/S。9轴姿态传感器还包含了I2C串行总线接口,支持标准和快速模式(100 kHz和400 kHz)及SPI串行接口标准。
规格参数
- 模拟电源电压范围:2.4V~3.6V
- 3轴加速度计:±2/±4/±6/±8/±16 g
- 3轴陀螺仪:±245/±500/±2000°/S
- 3轴磁力计:±2/±4/±8/±12高斯
- 16位的数据输出
- SPI/ I2C串行接口
- 嵌入式FIFO(先入先出的队列);
- 可编程中断发生
- 嵌入式自测试
- 嵌入式温度传感器
- 尺寸大小: 3.302cm x 1.524cm
- 重量大小:10g
使用方法
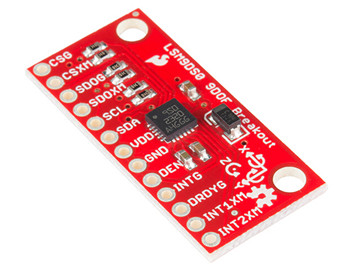
引脚定义
| 9轴姿态传感器 | 引脚定义 |
| CSG | 陀螺仪芯片操作方式选择引脚 |
| CSXM | 加速度芯片操作方式选择引脚 |
| SDOG | 地址选择引脚 |
| SDOX | SPI模式输出陀螺仪数据 |
| SCL | 信号时钟引脚 |
| SDA | 数据引脚 |
| VDD | 电源正极 |
| GND | 电源地 |
| DEN | 陀螺仪数据使能引脚 |
| INTG | 陀螺仪可编程中断 |
| DRDYG | 陀螺仪数据准备引脚 |
| INT1XM | 加速度中断1 |
| INT2XM | 加速度中断2 |
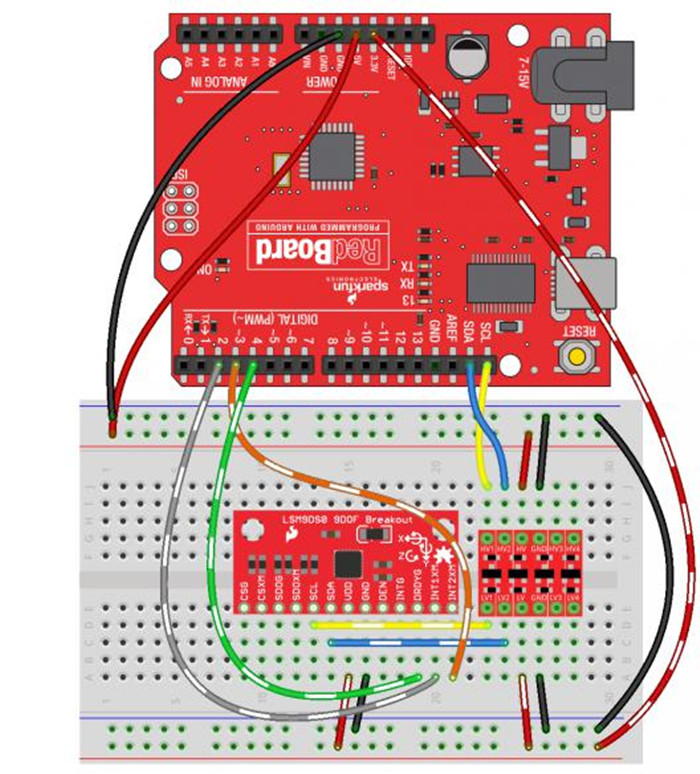
连接图示
首先需要安装一下LSM9DS0的Arduino库,然后图中右侧的小红色芯片为电平转换芯片。
| 9轴姿态传感器 | Arduino |
| CSG、CSXM、SDOG、SDOXM、DEN、INTG | 不接 |
| SCL | SCL |
| SDA | SDA |
| VDD | 3.3V |
| GND | GND |
| DRDYG | D4 |
| INT1XM | D2 |
| INT2XM | D3 |
应用例程
示例代码
#include <SPI.h> // Included for SFE_LSM9DS0 library
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SFE_LSM9DS0.h>
#define LSM9DS0_XM 0x1D // Would be 0x1E if SDO_XM is LOW
#define LSM9DS0_G 0x6B // Would be 0x6A if SDO_G is LOW
LSM9DS0 dof(MODE_I2C, LSM9DS0_G, LSM9DS0_XM);
const byte INT1XM = 2; // INT1XM tells us when accel data is ready
const byte INT2XM = 3; // INT2XM tells us when mag data is ready
const byte DRDYG = 4; // DRDYG tells us when gyro data is ready
boolean printRaw = true;
void setup()
{
// Set up interrupt pins as inputs:
pinMode(INT1XM, INPUT);
pinMode(INT2XM, INPUT);
pinMode(DRDYG, INPUT);
Serial.begin(115200); // Start serial at 115200 bps
uint16_t status = dof.begin();
Serial.println(status, HEX);
}
void loop()
{
printMenu();
while (!Serial.available())
parseMenu(Serial.read());
}
void printAccel()
{
if (digitalRead(INT1XM))
{
dof.readAccel();
Serial.print("A: ");
if (printRaw)
{
Serial.print(dof.ax);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.ay);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.az);
}
else
{
Serial.print(dof.calcAccel(dof.ax));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcAccel(dof.ay));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.calcAccel(dof.az));
}
}
}
void printGyro()
{
if (digitalRead(DRDYG))
{
dof.readGyro();
Serial.print("G: ");
if (printRaw)
{
Serial.print(dof.gx);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.gy);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.gz);
}
else
{
Serial.print(dof.calcGyro(dof.gx));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcGyro(dof.gy));
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(dof.calcGyro(dof.gz));
}
}
}
void printMag()
{
if (digitalRead(INT2XM))
{
dof.readMag();
Serial.print("M: ");
if (printRaw)
{
Serial.print(dof.mx);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.my);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.mz);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(calcHeading(dof.mx, dof.my));
}
else
{
Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.mx), 4);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.my), 4);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(dof.calcMag(dof.mz), 4);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(calcHeading(dof.mx, dof.my));
}
}
}
float calcHeading(float hx, float hy)
{
if (hy > 0)
{
return 90 - (atan(hx / hy) * 180 / PI);
}
else if (hy < 0)
{
return 270 - (atan(hx / hy) * 180 / PI);
}
else // hy = 0
{
if (hx < 0) return 180;
else return 0;
}
}
void streamAll()
{
if ((digitalRead(INT2XM)) && (digitalRead(INT1XM)) &&
(digitalRead(DRDYG)))
{
printAccel();
printGyro();
printMag();
}
}
void setScale()
{
char c;
Serial.println(F("Set accelerometer scale:"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 2G"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 4G"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 6G"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) +/- 8G"));
Serial.println(F("\t5) +/- 16G"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_2G);
break;
case '2':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_4G);
break;
case '3':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_6G);
break;
case '4':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_8G);
break;
case '5':
dof.setAccelScale(dof.A_SCALE_16G);
break;
}
// Print the gyro scale ranges:
Serial.println(F("Set gyroscope scale:"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 245 DPS"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 500 DPS"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 2000 DPS"));
// Wait for a character to come in:
while (Serial.available() < 1);
c = Serial.read();
// Use the setGyroScale function to set the gyroscope
// full-scale range to any of the possible ranges. These ranges
// are all defined in SFE_LSM9DS0.h.
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_245DPS);
break;
case '2':
dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_500DPS);
break;
case '3':
dof.setGyroScale(dof.G_SCALE_2000DPS);
break;
}
Serial.println(F("Set magnetometer scale:"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) +/- 2GS"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) +/- 4GS"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) +/- 8GS"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) +/- 12GS"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_2GS);
break;
case '2':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_4GS);
break;
case '3':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_8GS);
break;
case '4':
dof.setMagScale(dof.M_SCALE_12GS);
break;
}
}
void setRaw()
{
if (printRaw)
{
printRaw = false;
Serial.println(F("Printing calculated readings"));
}
else
{
printRaw = true;
Serial.println(F("Printing raw readings"));
}
}
void setODR()
{
char c;
Serial.println(F("Set Accelerometer ODR (Hz):"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) 3.125 \t 6) 100"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) 6.25 \t 7) 200"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) 12.5 \t 8) 400"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) 25 \t 9) 800"));
Serial.println(F("\t5) 50 \t A) 1600"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_3125);
break;
case '2':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_625);
break;
case '3':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_125);
break;
case '4':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_25);
break;
case '5':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_50);
break;
case '6':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_100);
break;
case '7':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_200);
break;
case '8':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_400);
break;
case '9':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_800);
break;
case 'A':
case 'a':
dof.setAccelODR(dof.A_ODR_1600);
break;
}
Serial.println(F("Set Gyro ODR/Cutoff (Hz):"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) 95/12.5 \t 8) 380/25"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) 95/25 \t 9) 380/50"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) 190/125 \t A) 380/100"));
Serial.println(F("\t4) 190/25 \t B) 760/30"));
Serial.println(F("\t5) 190/50 \t C) 760/35"));
Serial.println(F("\t6) 190/70 \t D) 760/50"));
Serial.println(F("\t7) 380/20 \t E) 760/100"));
while (Serial.available() < 1);
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_95_BW_125);
break;
case '2':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_95_BW_25);
break;
case '3':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_125);
break;
case '4':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_25);
break;
case '5':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_50);
break;
case '6':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_190_BW_70);
break;
case '7':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_20);
break;
case '8':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_25);
break;
case '9':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_50);
break;
case 'A':
case 'a':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_380_BW_100);
break;
case 'B':
case 'b':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_30);
break;
case 'C':
case 'c':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_35);
break;
case 'D':
case 'd':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_50);
break;
case 'E':
case 'e':
dof.setGyroODR(dof.G_ODR_760_BW_100);
break;
}
Serial.println(F("Set Magnetometer ODR (Hz):"));
Serial.println(F("\t1) 3.125 \t 4) 25"));
Serial.println(F("\t2) 6.25 \t 5) 50"));
Serial.println(F("\t3) 12.5 \t 6) 100"));
while (Serial.available() < 1)
;
c = Serial.read();
switch (c)
{
case '1':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_3125);
break;
case '2':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_625);
break;
case '3':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_125);
break;
case '4':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_25);
break;
case '5':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_50);
break;
case '6':
dof.setMagODR(dof.M_ODR_100);
break;
}
}
void printMenu()
{
Serial.println();
Serial.println(F("////////////////////////////////////////////"));
Serial.println(F("// LSM9DS0 Super Awesome Amazing Fun Time //"));
Serial.println(F("////////////////////////////////////////////"));
Serial.println();
Serial.println(F("1) Stream Accelerometer"));
Serial.println(F("2) Stream Gyroscope"));
Serial.println(F("3) Stream Magnetometer"));
Serial.println(F("4) Stream output from all sensors"));
Serial.println(F("5) Set Sensor Scales"));
Serial.println(F("6) Switch To/From Raw/Calculated Readings"));
Serial.println(F("7) Set Output Data Rates"));
Serial.println();
}
// parseMenu() takes a char parameter, which should map to one of
// the defined menu options. A switch statement will control what
// happens based on the given character input.
void parseMenu(char c)
{
switch (c)
{
case '1':
while(!Serial.available())
printAccel(); // Print accelerometer values
break;
case '2':
while(!Serial.available())
printGyro(); // Print gyroscope values
break;
case '3':
while(!Serial.available())
printMag(); // Print magnetometer values
break;
case '4':
while(!Serial.available())
streamAll(); // Print all sensor readings
break;
case '5':
setScale(); // Set the ranges of each sensor
break;
case '6':
setRaw(); // Switch between calculated and raw output
break;
case '7':
setODR(); // Set the data rates of each sensor
break;
}
}
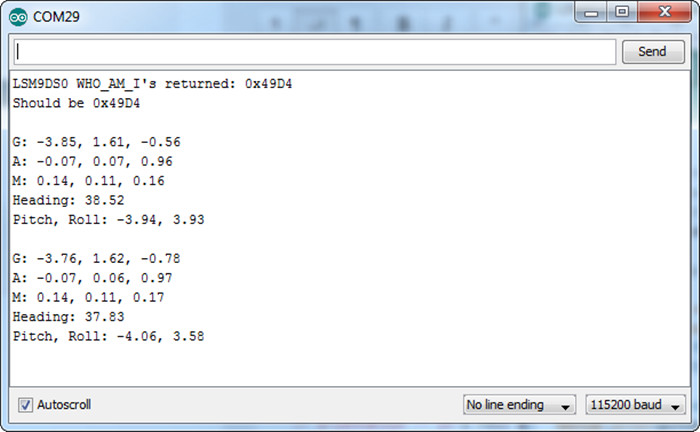
程序效果
下载完程序,然后打开串口监视器,将波特率调到115200,然后按照显示的内容输入相应数字进行功能选择,可以观察到多种数据。
产品相关推荐
产品购买地址
周边产品推荐
Arduino 9 Axes Motion Shield 9轴运动扩展板
相关问题解答
Arduino 9 Axes Motion Shield 9轴运动扩展板 三轴加速度计
相关学习资料
LSM9DS0- 9轴姿态传感器应用视频
电路原理图
数据表(lmv324)
LSM9DS0- 9轴姿态传感器官方操作手册
GitHub(设计文件)
奥松机器人技术论坛